What is geofencing and what are its advantages for businesses ?
Geofencing is a location-based technology usually used by B2C businesses to closely tailor the digital and physical experience of their clients. But, we’ll see in this article that the use of geofencing not only occurs in the marketing side of the selling process, it can be used for internal logistics, services efficiency, accessibility or customer satisfaction. Geofencing can be used in multiple sectors such as retail, hospitality, travel, fleet management, human resources and more. Services can be enhanced or created thanks to this technology.
In today's world, where nearly everyone carries a smartphone full of their favorite shopping, delivery or food apps, the potential of geofencing is expanding rapidly.
In this article, we're going to break down the meaning of geofencing and show you how it can help level up your business while keeping full control over your users' personal data as well.
What is geofencing?
The term “geofencing” comes from virtual boundaries called 'geofences' (literally “geographic fences”) positioned around physical spots like stores, malls, restaurants, event places or any areas you want to monitor. You can set them up based on distance, walking time or driving time from a specific spot. It’s like drawing a “circle” around a place using its geolocation (latitude and longitude).
The size and shape of these geofences are usually up to you and the location technology your using (GPS and/or beacons). It will depend on what you're trying to achieve but also on where it's located and if you have several spots you want to monitor in the same city.
So, when someone's phone steps in or out of one of these virtual zones (geofences), an event can be triggered and leveraged according to a defined use case. This event will then be sent to your platform and the information can be used to send push notifications, messages, making a mobile app do specific actions or for internal monitoring like counting visits and more.
How does geofencing work?
The system is rather simple: geofences can be created dynamically on a mobile app or retrieved from an API.
When using API, businesses usually go for a Software Development Kit (SDK) which is a bundle of presetted tools that ease the programming of geofence monitoring in mobile applications.
The SDK can either allow the setting of geofences but also the collection of users’ location data (latitude and longitude). Because geofence monitoring needs to access phone location, the users will have to accept at some point of their journey in the app to share their location.
Once done, the device gathers information in all available sources of location information including Global Positioning System (GPS), nearby Wi-Fi hotspots, cell towers, and IP Address. If no location permission is granted by the user, geofence monitoring is not possible. To ensure getting those permissions from users, the value proposition should be clear and relevant for them from the beginning of the digital journey.
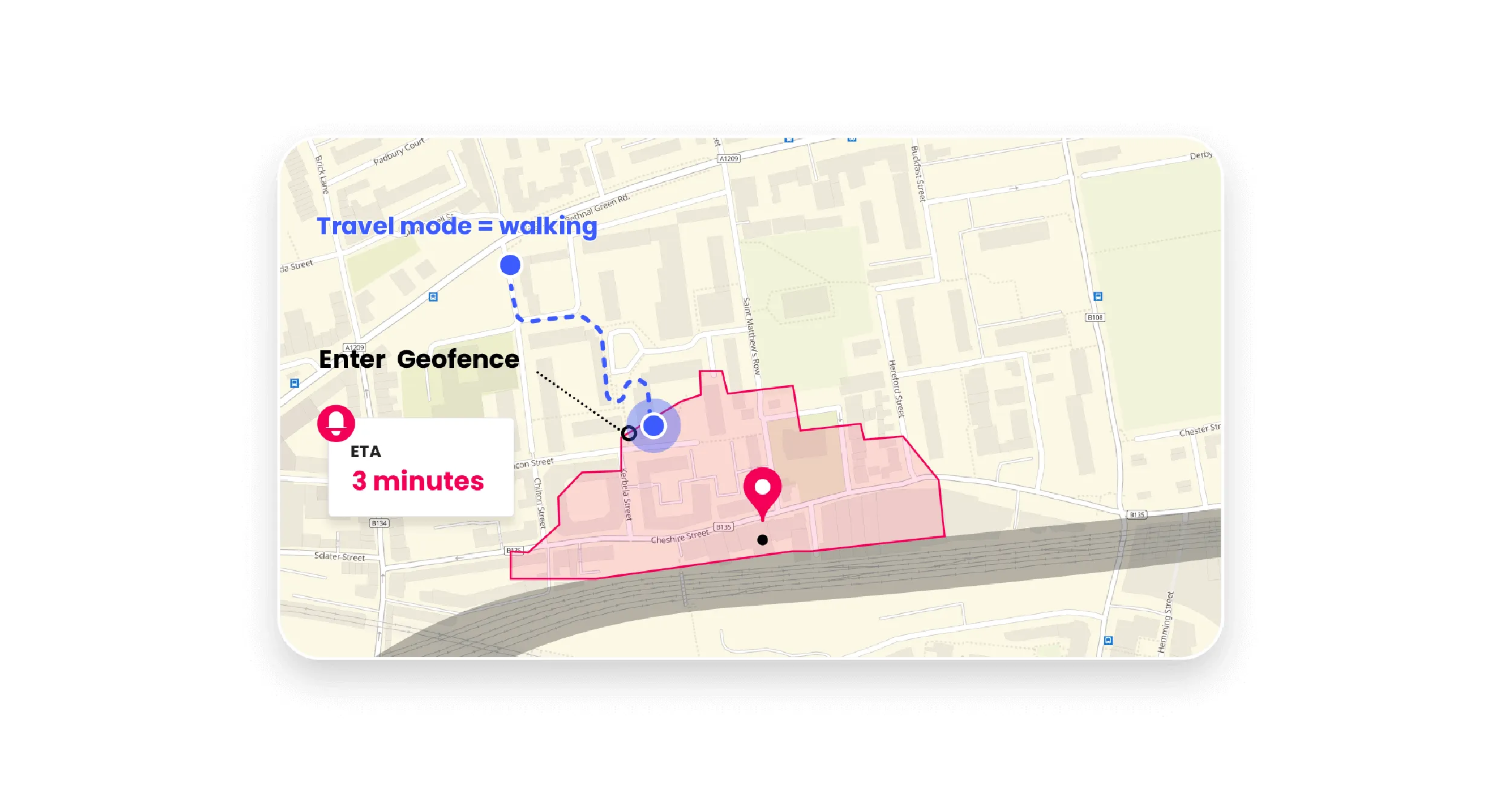
Properly set thanks to the SDK, location services allows to monitor the user's whereabouts, and give access to higher location accuracy even when the app is running in the background while minimizing battery drain. But the necessity for the highest accuracy in real-time updates varies depending on the use case. Is real time location or event relevant for your use case (delivery, click&collect, etc)? Or do you just need to know at what time and where the user crossed your geofences for targeted messages or users’ behavior analysis?
Geofencing SDK usually proposes different tracking profiles to cleverly combine location accuracy and real time monitoring: passive tracking (with lower accuracy but less battery impact), visit tracking (medium accuracy) and live tracking (high accuracy but higher battery usage).
You can tailor between profiles during the customer journey. For example, a restaurant app might want to set a Live Tracking profile when the client has made their order and is walking toward the restaurant, then stop tracking when he picks up the order. Same goes with food delivery, you will need to know when the driver is in the restaurant area and when he leaves to tell the client that the meal is on its way!
What about the collect of personal data?
In a study made by ZipDo, they found that “80% of consumers are willing to share location data with apps that provide a valuable service”.*
Every SDKs used for geofence monitoring differ on the way they handle users’ location and other personal data. They can collect and send the location information to backend solutions (supplier’s servers) that would process or collect the data or, they can process it locally in the app of each user itself.
In the first case, data can be processed backendside by third party providers generating data privacy questions. In the second case, user data does not leave users’s phones.
Nevertheless, the owner of the app remains in full control of those data and as a client, you should check where your data is going to protect your users.
At Woosmap, we personally chose to have a privacy-first approach so when using our Geofencing SDK, all data remains locally in the app itself. For example, our solutions as so transparent that Woosmap doesn’t even have to be declared as data manager, as there is no data to handle on our side.
Tangible examples of geofencing usage
The uses of geofencing are vast and new ones are being created every day in every sector. To only name a few, here is a non-exhaustive list of use cases.
- Retail: send mobile notifications when a visitor enters your boundary, or is nearby, to push your promotions, products or services. You can also customise the customer experience after detecting recurrent visits and provide tailored services or promotions.
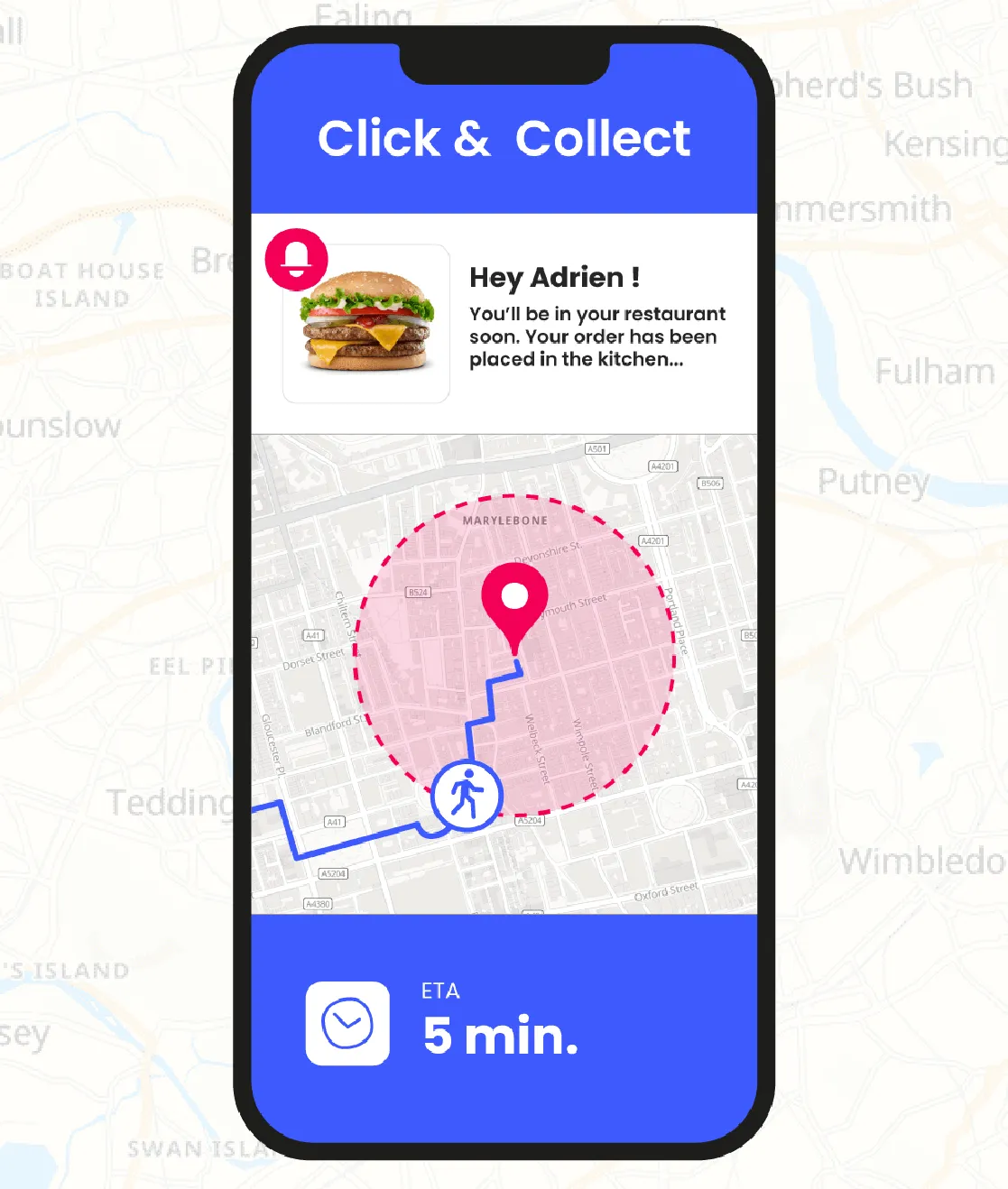
- Food: prepare Click & Collect orders at the right time (when the clients cross a certain geofence) to prepare it in time and deliver a hot meal.
- Fleet Management: keep track of your driver’s progresses around its route.
- Hospitality/Hotel: know if your visitors are near to be ready to welcome them, and make sure their room is ready..
- Fraud detection: link your users’ location when withdrawing cash for more security.
- Deliveries: check if the driver is approaching the restaurant and then track them around the final point to know if the order will be then delivered in the ETA period to the client.
- Human Resources: on a high security level site, know if everyone that arrived left the place as intended.
- Insurance: propose travel insurance to customers that spend time in airports.
- Promotional campaigns: push your ads in a defined area, usually near your store.
- Events/Tradeshow: push mobile notifications for people near your stand or near the event.
The Top 5 Advantages of Geofencing
Incorporating geofencing into your company’s strategy can lead to enhanced precision, cost savings, data-driven decisions, personalized customer experiences, and a distinct competitive advantage in the market. It's a versatile tool that can change the way you engage with your audience on a daily basis.
1. Enhanced Precision in Targeting
Geofencing is useful for businesses looking to target people in precise areas. Whether you have physical shops, venues, offices, or other locations, you can engage potential customers (or collaborators) and encourage them to visit your premises. This level of precision not only increases foot traffic but also improves the chances of converting prospects into loyal customers (or into employees), depending on the sector.
For example, geofencing could be used for a job offer. Targeting a specific area to attract profiles not far from an office, or from a specific job convention or a shop could be more effective than just mentioning the location of the job when posted on your website.
2. Cost-Effective Campaigns & Location Based Advertising
One of the advantages of geofencing is its cost-effectiveness in marketing campaigns. By reaching the right person at the right time on the right channel, you can significantly enhance the efficiency of your marketing efforts.
It eliminates the need to pay for misdirected ads at large scale and allows you to allocate your budget more wisely. You can target individuals who are in close proximity to your shops, ensuring that your call to action reaches those who are most likely to respond. Moreover, calls to action have more chance to be more effective and special coupons more used as they are sent in real-time and promote close-by products.
3. Enhanced Data Collection Capabilities
Geofencing doesn't just boost your marketing efforts; it also boosts your data collection capabilities. You can gain valuable insights into foot traffic, dwell times, conversion rates, click ratio and more.
This data can be integrated with information about users' online activities, purchase behaviors, and browsing habits. With this comprehensive dataset, marketers can personalize campaigns and optimize user experiences, ultimately leading to increased customer engagement and satisfaction.
4. Personalised Customer Experiences
The location-based tool enables businesses to tailor the customer experience based on the user's area. For instance, in the retail industry, when offering Click & Collect services, knowing when a customer is near the pickup point can be invaluable for streamlining the process.
Sending a notification when they're in close proximity makes it convenient for them to drop by and try your latest products or services. In the study “Essential Location Based Marketing Statistics In 2023” made by ZipDo, 77% of consumers said they would be more likely to engage with ads if they were tailored to their location*!
The result is a more personalised and convenient shopping experience that promotes customer loyalty. It also enhances internal logistics on the other side and automates even faster services.
5. Competitive Edge
In today's competitive landscape, staying ahead of the curve is crucial. Geofencing can give you a significant competitive edge. For example, in the fast-food industry, monitoring customers' devices to identify when they're nearby allows you to, first send CTA before your competitors, and then prepare orders in advance. This not only ensures you to talk to users before your competitors, but also ensures that they receive a hot meal quickly without unnecessary wait times. It is key to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
We could also give an example of the hospitality sector. Using geofencing could mean better preparing for customers arrival, making sure that their bedroom is ready before arrival.
The insurance sector could also be used as an example. As everyone has insurance for their home or their car, the client’s profile risks could be tailored to their exact position. If they’re far from their home, the profile risk is higher and vice versa.
Going further with Beaconing: Monitor your indoor venues
After using geofencing in outdoors, you can also use another location-based technology inside the geofencing solution, to monitor indoor venues on different levels using beacons. It was made for locations with bad GPS signal or multi-floor buildings.
Beacons are devices positioned inside a location (shop, tradeshow, convention…) that transmit location-triggered notifications on (and to) smartphones nearby. This is a solution used in retail, hospitality, healthcare, museums etc. for enhancing the user experiences but also for businesses to gather valuable data on their visitors.
Coupled with a geofencing strategy, you can send push notifications on close products but also measure the impacts of your campaigns and actions with data such as:
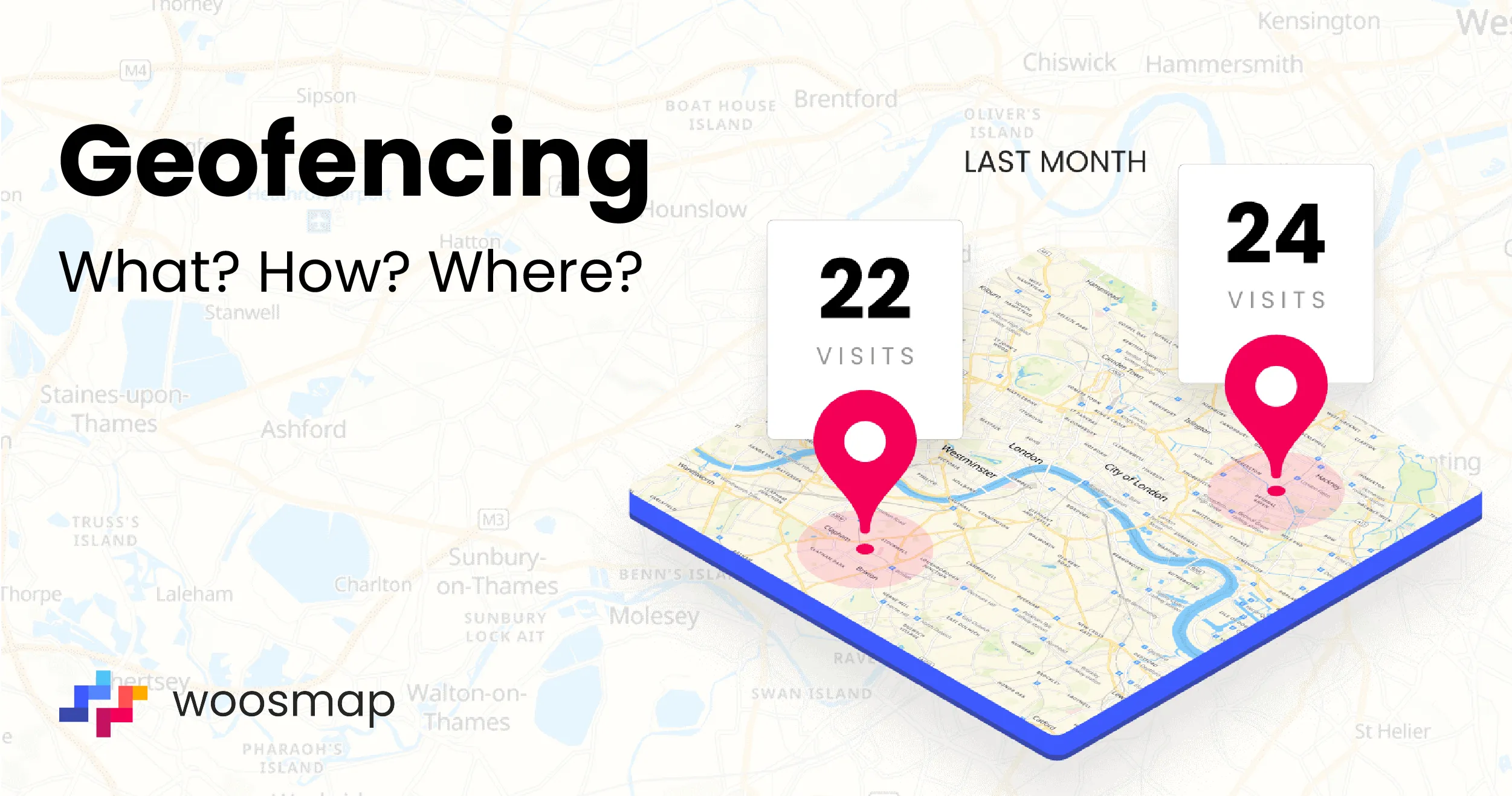
- How many visits it attracted to your venue (when users enter and exit),
- The number of visits to specific locations (selection of a panel of shops to be studied for example) or areas (in a big store),
- The number of visits to the venue after clicking on the notification,
- Or even the time spent at the location and repeated visits.
*Study “Essential Location Based Marketing Statistics In 2023 “ from ZipDo